Search This Supplers Products:steel flangesCarbon steel pipe elbowssteel pipe teessteel pipe redcuerssteel pipe capspipe bends
Mechanical properties of metal materials and heat treatment process
Mechanical properties of metal materials and heat treatment process (1)
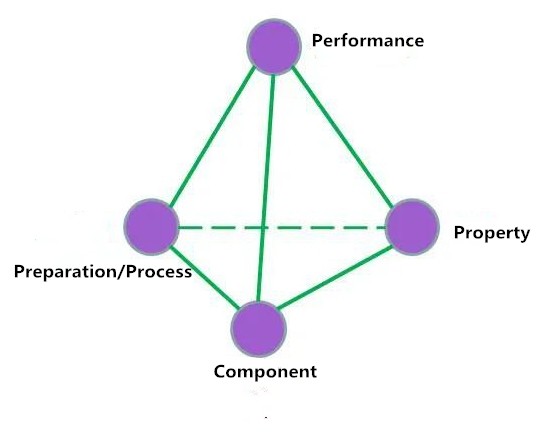
Mechanical properties of materials
The mechanical properties of the material refer to the behavior under the action of an applied load (external force) or a combination of load and environmental factors (temperature, medium, and loading rate).
Mechanical properties of metal | Commonly used mechanical performance index of metal |
Strength | Yield strength, tensile strength, fracture strength |
Plasticity | Percentage elongation,reduction of area, work-hardening exponential |
Springiness | elasticity modulus,elastic limit,proportional limit |
Hardness | BH, Vickers hardness,Rockwell hardness |
Toughness | static toughness, impact toughness, fracture toughness |
Fatigue | fatigue strength, fatigue life, fatigue notch sensitivity |
Stress corrosion | Stress corrosion critical stress field intensity factor,Stress corrosion cracking rate |
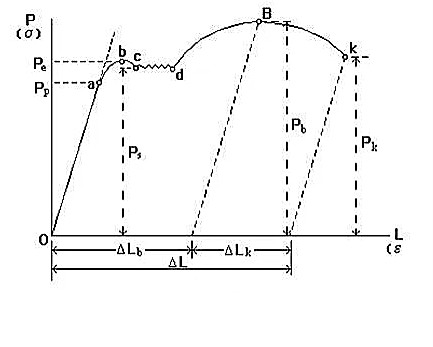
Unidirectional static tensile stress of MS--- stress-strain curve
2、 abpart:elastic deformation +Plastic Deformation
3、 bcd part:the material has obvious plastic deformation,under the condition that the force is basically unchanged, the sample continues to elongate
4、 dB part:Elastic deformation + uniform plastic deformation
5、Point B, the phenomenon of neck shrinkage occurs, the local section of the sample obviously reduces the bearing capacity of the sample, the tensile force reaches the maximum value, and the sample is about to fracture.
1. Strength refers to the ability of a material to resist plastic deformation and fracture。
Yield Strength
Δs= Fs/So
Fs: The tensile force that the sample bears when yielding (N)
So: Original cross-sectional area of the sample (mm)
2. Tensile strength
The maximum tensile stress that the specimen withstands before breaking off reflects the resistance of the material to the largest uniform deformation.
Δb=Fb/So
Δb is often used as a seat for brittle materials and as a basis for design.